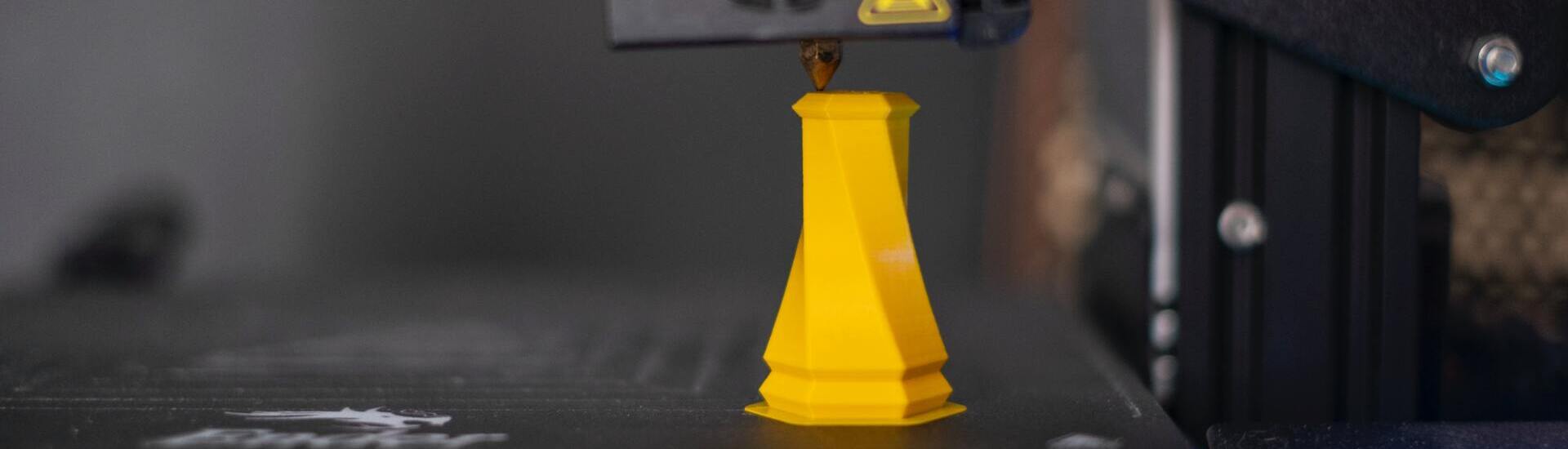

Product Design Engineering (Engenharia da Conceção e Desenvolvimento do Produto)
Product Design Engineering (Engenharia da Conceção e Desenvolvimento do Produto)
Programme Content
The development of innovative products is a critical factor for competitiveness. Currently there is a trend towards shorter product lifetimes, as a consequence of changes in consumer demand patterns. In this context, the challenges posed to companies in terms of the quality of their products are accompanied by challenges in terms of effectiveness and efficiency of the underlying design processes.
There is an opportunity for Portuguese companies to evolve in the value chain, from producers to creators of products, with high quality, added value and taking into account sustainability principles. The Master aims to provide its graduates with an integrated set of skills, in the field of developing quality products, quickly and innovatively, with a high degree of success and added value. These are solidly grounded in knowledge and understanding capabilities of advanced level in the scientific area of Mechanical Engineering and in particular in the field of design and product development.
They are intended to be evidence of knowing how to integrate knowledge, how to apply it, how to delimit and solve problems, how to communicate, how to select and collect/produce information in a professional manner, as well as how to learn autonomously throughout life.
The course also enables professionals already in the labour market to obtain a specialization in this area that will increase their technical competences and help the entrepreneurial and industrial dynamization of this region surrounding the Polytechnic of Leiria.
Programme Introduction
Unique Aspect of the programme
An unique aspect of the Masters in Product Design Engineering is the Global Work – a work of product design and development that aims to apply and reinforce the skills acquired in all the curricular units.
The course units’ contents, as well as their sequence and placement are designed to provide the support to students in the development of this work.
The theme of the work is defined by the students, and there are specific classes for developing ideas and generating concepts. The student is thus invited to take an active part in defining his Global Work.
This approach contributes to a better fit between each student’s skills, expectations and the potential for innovation and level of development for the work. At the same time, it allows the development of very diverse works, but which retain key elements of this course, such as sustainability, in its matrix.
Programme Coordinator
Fábio Jorge Pereira Simões
coord.mecdp.estg@ipleiria.pt
Reference
School
City
Language
Type
Length
Vacancies
General and International student contingent: 20
Notice
Edital 2025 2v
Edital 2025 2v (PT Doc)
DGES certification
Objectives
The Master aims to provide its students with
- An integrated set of dynamic skills, solidly grounded in technical and scientific knowledge essential to the development of quality products in a fast and innovative way, with a high degree of success and added value;
- A multidisciplinary and versatile education, allowing the professional to perform strategic and/or supervisory functions in industrial or service companies, as well as public or private entities;
- Opportunities to launch their professional career through an internship, collaborate with companies in the development of a project or dissertation, or pursue a career in scientific research.
Study Plan
- 1st Year
- 2nd Year
| ID | Name | Semester | ECTS | Length |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Product Design | 1st Semester | 5 | 45 h | |
|
The development of innovative products is a fundamental process as a factor of competitiveness. Increased competition, rapid technological changes, the reduction of life cycle of products and greater demand from consumers require businesses agility, productivity and quality which necessarily depend on the efficiency and effectiveness of the company in this process. In an industrial cluster as the Portuguese, mainly focused on producing components to incorporate in products from outside, it is essential to seek to intervene in the development of its own products, innovative, sustainable, and high added value. This course will provide to the student the acquisition of skills in the field of general product design, innovative product development and ergonomics. This unit will enable students to perform the following tasks in the scope of the Global Work:
Syllabus: 1. Development of new products 1.2 Product Development Process 1.3 Market analysis (identifying the need for new products and limitations of existing products) 1.4 Characterization and Product Specifications 2. Creativity and innovation 2.1 Creative environments 2.2 Tools and techniques to support creativity 2.3 Biomimicry as a source of inspiration 3. Theories of Product Design 3.1 Concept of Design. Areas of Design. Interdisciplinary Design Product 3.2 The value of the product 3.3 Semiotics of product 3.4 Color, shape, texture 3.5 Eco-Design, Sustainable Design, Inclusive Design. 4. Anthropometry and Ergonomics 5. Design for X | ||||
| Sustainable Design | 1st Semester | 5 | 45 h | |
|
This course aims to present some methodologies that support the sustainable design process of products and processes, as well as some of the existing techniques which can be applied to the different stages of design process. The main objective of this course is to allow the acquisition of necessary knowledge to apply the methodologies and technics to product design. The intention of sustainable design is to “eliminate negative environmental impact completely through skillful, sensitive product design”. This unit will enable students to perform the following tasks in the scope of the Global Work:
Syllabus: 1. Sustainable Design: definitions and concepts: 1.1. Principles of Sustainable Design 2. Nature Design: Biomimicry 3. Engineering Sustainability 4. Lifecycle Assessment, Eco-design and Eco-indicators 5. Environmental Impacts of Materials, Green Materials and Resource Management Technologies 6. Natural Resources and Sustainability: 6.1. Sustainable Water and Wastewater Systems 6.2. Applied Renewable Energy Technologies, Energy Management and Power Systems | ||||
| High-Performance Materials | 1st Semester | 5 | 45 h | |
|
The subject of High Performance Materials intends to develop the basic knowledge level on materials science students possess after graduate level. Students are taught to apply systematic material selection procedures, to learn about and investigate innovative materials and the respective technologies, within domains such as biomaterials and natural materials, as well as to assess the performance of materials for engineering applications, to combine different materials in applications requiring specific characteristics in fields as diverse as electronics, medicine, aerospace, automotive, etc. This unit will enable students to perform the following tasks in the scope of the Global Work:
Syllabus: 1 Materials Review 1.1 Materials for Engineering Applications: Mechanical and Physical Properties 2 Materials Selection 2.1 Selection by Function 2.2 Selection considering shape 2.3 Selection of composite materials 3 Biomaterials 3.1 Definitions and fields of application 3.2 1st, 2nd, 3rd and 4th generation biomaterials 4 Porous and Cellular Materials 4.1 Polymeric foams 4.1.1 Properties 4.1.2 Production techniques 4.2 Natural cellular materials 4.2.1 Wood 4.2.2 Cork | ||||
| Product Modelling and Simulation | 1st Semester | 5 | 45 h | |
|
In this unit, it is intended that students acquire modeling and simulation skills. Also to develop mathematical models to create geometric modeling, to program linear finite element problems, to interpret and compute structural problems using commercial software and to make an isogeometric analysis starting from geometric model and using numerical methods. Syllabus: 1 – Geometric modeling 2 – Programing the finite element method 3 – Introduction to non-linear problems This unit will enable students to perform the following tasks in the scope of the Global Work:
| ||||
| Marketing of New Products | 1st Semester | 5 | 45 h | |
|
This unit intends to provide knowledge about creativity, innovation, marketing and strategy, necessary for the formulation of a marketing plan. Thus, in this unit students are taught how to define and distinguish the concepts of Marketing, understand the process of innovation and marketing and its importance in business success, perceive the importance of marketing and innovation as a competitive advantage generator. During classes, students will develop the capacity to generate, discuss and implement new ideas and recognize market opportunities; demonstrate binding of the marketing practices to release successful new products, develop skills that allow them to be reviewed individually and in groups, as players of the creative process. They also will relate innovation and competitive advantage, formulate marketing strategies and assess organizations towards the innovative process development and the company’s products competitiveness. This unit will enable students to perform the following tasks in the scope of the Global Work:
Syllabus 1. Introduction 2. Creativity and product development 3. Innovation Management 4. The Marketing Plan | ||||
| Introduction to Research | 1st Semester | 5 | 45 h | |
|
The attendance of a master entails the development of a scientific work, so students have the opportunity to become familiar with of scientific research. It is intended for students to develop basic notions on the methodology of scientific research, so that they understand science as a process of production and communication of knowledge; it is also intended to provide tools for the student to write and present academic work with accuracy, systematization and critical spirit, encouraging the practice of standardization of criteria in the methodology of citation / referencing. This unit will enable students to perform the following tasks in the scope of the Global Work:
Syllabus Basics of Scientific Research Qualitative and quantitative research The process of research Communications and Texts for the Scientific Community Library resources Writing of scientific texts Publishing scientific texts Research Project Scientific Research in Portugal Intellectual Property | ||||
| Performance of Mechanical Components | 2nd Semester | 5 | 45 h | |
|
This curricular unit will supply the student with general competencies in the area of the mechanical behaviour of components in service as well as in the area of material selection for engineering applications. The student will be taught to characterize materials in terms of strength, fracture and fatigue, and to select materials and polymer matrix composites for engineering applications. This unit will enable students to perform the following tasks in the scope of the Global Work:
Syllabus 1. Materials used in the manufacture of mechanical components 2. Composite materials and polymer matrix composites 2.1. Classification and processing techniques 2.2. Physical and mechanical properties 3. Mechanical behaviour 3.1. Fracture and Impact 3.1.1. Key Concepts 3.1.2. Experimental Procedures 3.2. Fatigue 3.2.1. Key Concepts 3.2.2. Fatigue Tests 3.2.3. Propagation of fatigue cracks 3.3. Creep | ||||
| Prototyping and Rapid Manufaturing | 2nd Semester | 5 | 45 h | |
|
This unit aims the acquisition of knowledge regarding the most advanced manufacturing technologies and unconventional industrial processes as well as the specifics associated with each of them. The student is taught to understand and use modern rapid prototyping systems, to select the processing parameters best suited to the production of prototype quality, to understand and use modern manufacturing systems quickly and micro-fabrication and to understand the importance of nanotechnology in the technical aspects, ethical and social. This unit will enable students to perform the following tasks in the scope of the Global Work:
Syllabus: 1. Rapid prototyping processes – Steps manufacturing – Stereolithography processes – Sintering – Extrusion – 3D Printing – Mixed Processes – Recent Developments 2. Rapid Manufacturing Processes: Direct techniques; Indirect techniques; Hybrid techniques 3. Micro-fabrication – Micro-injection – Procedures for removal of material: lithographic and non-lithographic – Processes additives: photo-polymerization and sintering – Hybrid Processes – Process for the production of micro-components 4. Nanotechnologies | ||||
| Energetic Efficiency and Environment | 2nd Semester | 5 | 45 h | |
|
It is intended that students get general and specific knowledge, about the main directions used in the field of Energy and Rational Use of Energy/Electrical Efficiency (RUE/ EE) and the main trends to better understand and frame the importance and true potential of ERU/ EE the future of the energy sector. Students are also taught about the principles of sustainable development., and to interpret and recognize sustainable energy systems. This unit will enable students to perform the following tasks in the scope of the Global Work:
Syllabus 1) Introduction to the Concept of Sustainable Development (SD) 2) Sustainable Energy Systems 3) Renewable Energy 4) Data Energy in Portugal 5) Data Energy in the World 6) Energy Efficiency 7) Energy Diagnosis – Compressed Air | ||||
| Recycling | 2nd Semester | 5 | 45 h | |
|
The curricular unit of the Master in Product Design Engineering aims providing the student with the acquisition of competences related to recycling of the different kind of materials. The student is taugth to: – Know the terminology, concepts, perspectives and tools of recycling. – Define strategies for the development of methodologies in the aim of materials. Reduction / Reuse / Repair / Recycling. – Identify the most appropriate methodologies and techniques for recycling different kind of materials. – Optimise resources, processes and products obtained by recycling. – Answer to emergent solicitations of the market and services in the aim of materials recycling. This unit will enable students to perform the following tasks in the scope of the Global Work:
Syllabus: 1. Introduction to recycling 1.1 General concepts 1.2 Advantages of recycling 2. Perspectives and legal framework of recycling 3. Recyclable and non-recyclable materials 4. Solid Urban Waste 4.1 Treatment Processes 4.2 Composting 4.3 Incineration and co-incineration 5. Recycling polymeric, metallic, ceramic and composite materials 5.1. Raw materials and respective classification 5.2. Treatment, processes, techniques and equipment recycling 6. Applications of recycled materials 7. Trends and prospects for recycling | ||||
| Advanced Production Technologies | 2nd Semester | 5 | 45 h | |
|
The unit of Advanced Production Technologies intends to extend the basic skills about production processes in the sense of understanding less conventional processes, applicable to cases of greater specificity and / or demand. It is intended particularly to present the student general knowledge about unconventional machining and joining processes, and the basics of Design for Manufacturing. This unit will enable students to perform the following tasks in the scope of the Global Work:
Syllabus:
| ||||
| Automation and Robotics | 2nd Semester | 5 | 45 h | |
|
This curricular unit provides the student with a general knowledge in the scientific and technologic area of automated systems. It brings into the master programme two different components within this area of knowledge which should always be present in the process of product development. The first one gives the student a general view of the different technologies and methodologies currently used in the automation of some functions of a product and the second focuses on the processes of production automation. The unit allows an overview of the field, necessarily not very deep,with the methods, technologies and applications currentrly in use in the automation of industrial processes. The general objectives are:
This unit will enable students to perform the following tasks in the scope of the Global Work:
Syllabus: General notions on automatic systems Notion of system System analysis Controller synthesis Sensors and instrumentation Basic notions on instrumentation Sensors Signal conditioning Automatic industrial systems Basic definitions Command part and operating part The programmable logic controller and its applications Introduction to robotics Industrial robots Mobile robots Advanced robotics | ||||
| ID | Name | Semester | ECTS | Length |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dissertation/Project | Annual | 60 | ||
a) Students choose to carry out a project / dissertation work or a professional internship, under the terms to be regulated by the legal and statutory body of the higher education institution. | ||||
Entry Requirements
People who can apply to the Master’s Degree:
- Holders of an undergraduate degree or a legal equivalent in engineering and related fields, industrial design, and product design;
- Holders of a foreign higher education diploma, granted after a first cycle of studies, under the principles of the Bologna Process, by a State, which has subscribed this Process, in engineering and related fields, industrial design, and product design;
- Holders of a foreign higher education diploma that is recognized as meeting the objectives of an undergraduate degree by the Technical and Scientific Council of the School of Technology and Management, in engineering and related fields, industrial design, and product design;
- Holders of an academic, scientific or professional curriculum that is recognized as certifying the skills to attend this cycle of studies by the Technical and Scientific Council of the School of Technology and Management;
- Students who are close to completing their undergraduate degree in the field required for entering the Master’s degree, and declare it in their application
International Student
All information related to the international student application should be consulted on our International Students webpage.
.
People who can apply to the Master’s Degree:
- Holders of an undergraduate degree or a legal equivalent in engineering and related fields, industrial design, and product design;
- Holders of a foreign higher education diploma, granted after a first cycle of studies, under the principles of the Bologna Process, by a State, which has subscribed this Process, in engineering and related fields, industrial design, and product design;
- Holders of a foreign higher education diploma that is recognized as meeting the objectives of an undergraduate degree by the Technical and Scientific Council of the School of Technology and Management, in engineering and related fields, industrial design, and product design;
- Holders of an academic, scientific or professional curriculum that is recognized as certifying the skills to attend this cycle of studies by the Technical and Scientific Council of the School of Technology and Management;
- Students who are close to completing their undergraduate degree in the field required for entering the Master’s degree, and declare it in their application
International Student
All information related to the international student application should be consulted on our International Students webpage.
.
Accreditation
State: Accredited
Number of years of accreditation: 6
Publication date: 04-12-2020
Accreditation A3ES
State: Accredited
Number of years of accreditation: 6
Publication date: 04-12-2020
Accreditation A3ES
More Information
Contacts
E-mail: studywithus@ipleiria.pt
Contacts
E-mail: studywithus@ipleiria.pt

Application Fee
60€
Enrolment Fee
General Contingent: 50€
International student contingent: 100€
General Contingent: 50€
International student contingent: 100€
Tuition Fee
General Contingent: 697 €
International student contingent: 3000€
General Contingent: 697 €
International student contingent: 3000€